Toxins of the Venom of Tarantulas (Theraphosidae, Arachnida) in the Interspecies Interactions
Abstract
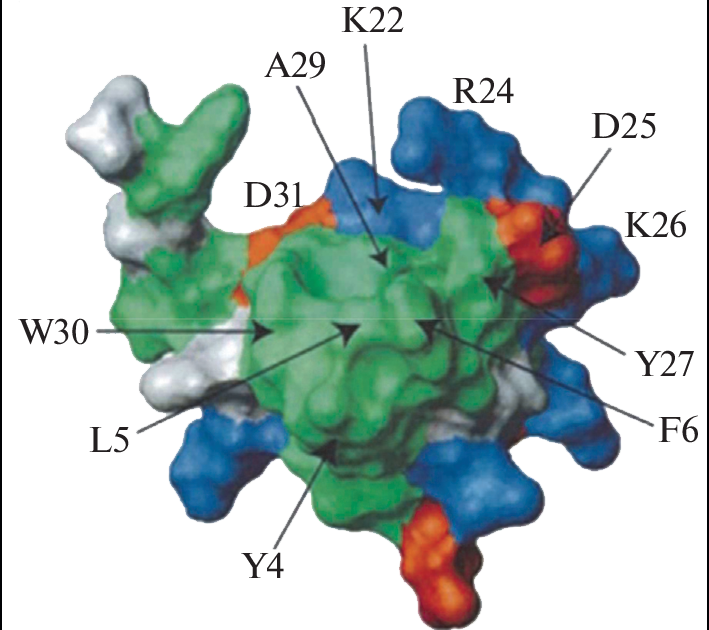
Spiders are the most important entomophagous animals in ecosystems. They are also the most numerous poisonous animals on the planet, and they are indispensable regulators of populations, killing mainly insects and other small arthropods. Spiders are an integral part of the food chain; they produce venom serving to immobilize the prey. Spider venoms are a “natural combinatorial library” of biologically active substances, with varying effectiveness and specificity. A feature of the biological effect of the spider’s venom is a unique combination of the low toxicity of the whole venom, for both animals and humans, with high selectivity of the interaction of the neurotoxins, which are part of the venom, with the molecular structures of ion channels and synaptic receptors of the nervous system. The present review introduces new fundamental facts, ideas, and perspectives of the practical application of spider venoms in biomedical research and drug design. The current state of research on a unique set of polypeptide toxins, serving as chemical factors (allomons) of the interspecific (allelochemical) interactions of spiders of the family Theraphosidae, is considered. Up-to-date information on the structure of spider venom toxins is analyzed using the UniProt database. The latest bioecological and toxicological characteristics of tarantulas are presented. The chemical nature and mechanism of action of some unique toxins selectively acting on key processes in the nervous system are considered. The toxins act upon synaptic transmission and the functioning ion channels, which allow spiders both to interact with various molecular targets of the prey or predator and to implement various life strategies, gaining an evolutionary advantage.
Gelashvili, D.B., Romanova, E.B. Toxins of the Venom of Tarantulas (Theraphosidae, Arachnida) in the Interspecies Interactions. Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 52, 214 (2025).