Procoagulant Effects of Bothrops diporus Venom: Kinetic Modeling and Role of Serine Protease Activity
Abstract
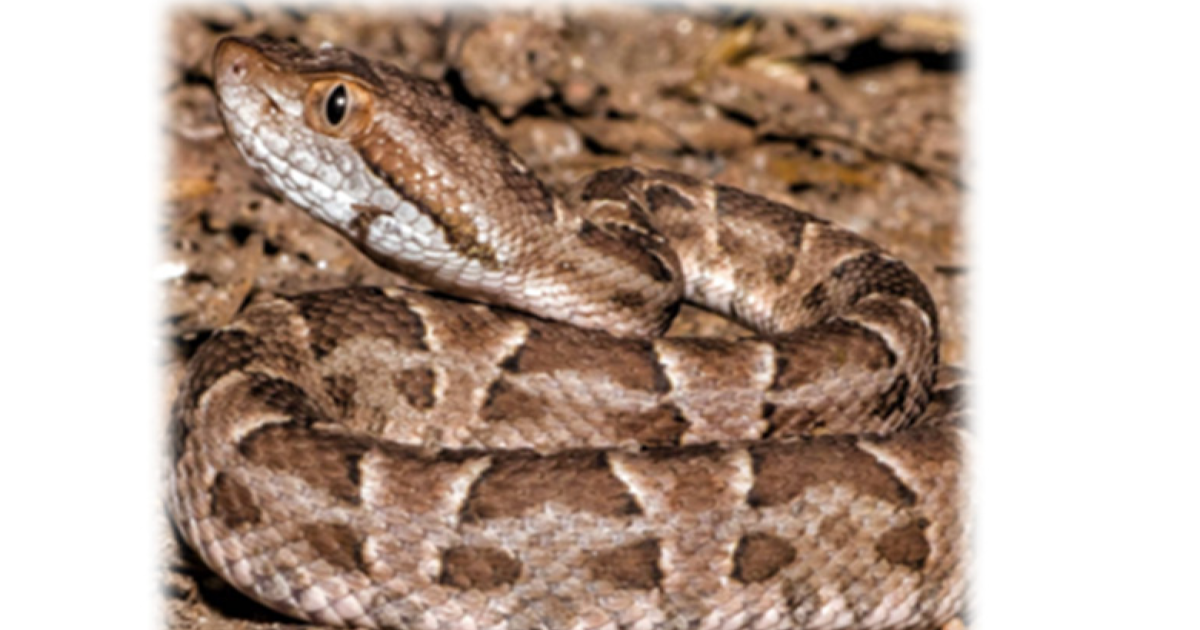
Bothrops species are responsible for the majority of envenomations in Argentina. In particular, Bothrops diporus is among the main species responsible for the majority of envenomations in Argentina and causes significant injury and coagulopathy. Given the significance of this venom, the authors sought to define the toxin responsible for coagulopathy with specialized spectrophotometric and thromboelastographic methods. Utilizing clotting time, spectrophotometry, and thromboelastography, it was determined that B. diporus venom has potent, procoagulant activity in human plasma and buffer milieu. Calcium-dependent and -independent activities consistent with serine protease activity were identified. The activity included both thrombin-generating and thrombin-like enzymatic activity. The venom cleaved the serine protease-specific chromogenic substrate β-Ala-Gly-Arg-p-nitroanilide diacetate, and its activity was inhibited in plasma by antithrombin after addition of heparin. Further, venom exposed in isolation to RuCl3, a known inhibitor of serine protease-containing venoms, demonstrated decreased activity in human plasma. In conclusion, the present study contributes to a better understanding of B. diporus venom and may have implications for the rational design of inhibitors, antivenom formulations, or preclinical models to study venom-induced coagulopathies.